Cooling tower selection method
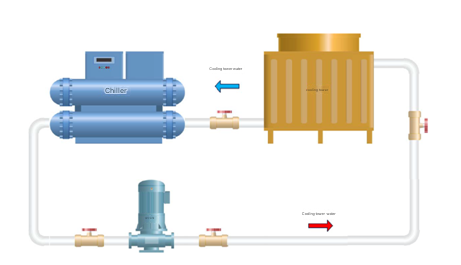
Introduction to cooling tower selection parameters and reasonable capacity
1. Inlet water temperature: cooling tower inlet water temperature, unit ℃.
2. Outlet water temperature: cooling tower outlet water temperature, unit ℃.
3. Wet bulb temperature: Thermodynamic wet bulb temperature (adiabatic saturation temperature) refers to the temperature of the system when a large amount of water is in contact with limited wet air under adiabatic conditions, and the latent heat required for water evaporation comes entirely from the sensible heat released by the decrease in the temperature of the wet air. The wet bulb temperature is determined by the dry bulb temperature, relative humidity and atmospheric pressure (the wet bulb temperature can refer to the HVAC design manual value), unit ℃.
4. Processing capacity: the cooling water flow rate processed by the cooling tower per unit time, unit m³/h.
5. Approximation: the difference between the outlet water temperature and the wet bulb temperature, unit ℃.
Example: National standard 5 degree difference 100 tons cooling tower, that is, 37℃-32℃-28℃-100m³/h, inlet water temperature 37℃, outlet water temperature 32℃, wet bulb temperature 28℃, approximation degree 32℃-28℃=4℃, inlet and outlet water temperature drop 37℃-32℃=5℃, 100 tons of cooling water are processed in one hour, commonly known as 100 tons cooling tower.
Reasonable volume release: In order to cope with extreme climate conditions (high humidity, high temperature) and cooling tower cooling efficiency attenuation after years of use, reasonable volume release is required.
When selecting, the heat generation unit of the heat generating equipment is 1, the water pump should be released by 1.2, and the cooling tower selects the flow corresponding to the water pump, which is 1.2.
Example: The main condenser flow is 100m³/h, the water pump uses 120m³/h, and the cooling tower also selects the volume release parameter of 120m³/h.
A total of 1 page 1 data